Introduction:
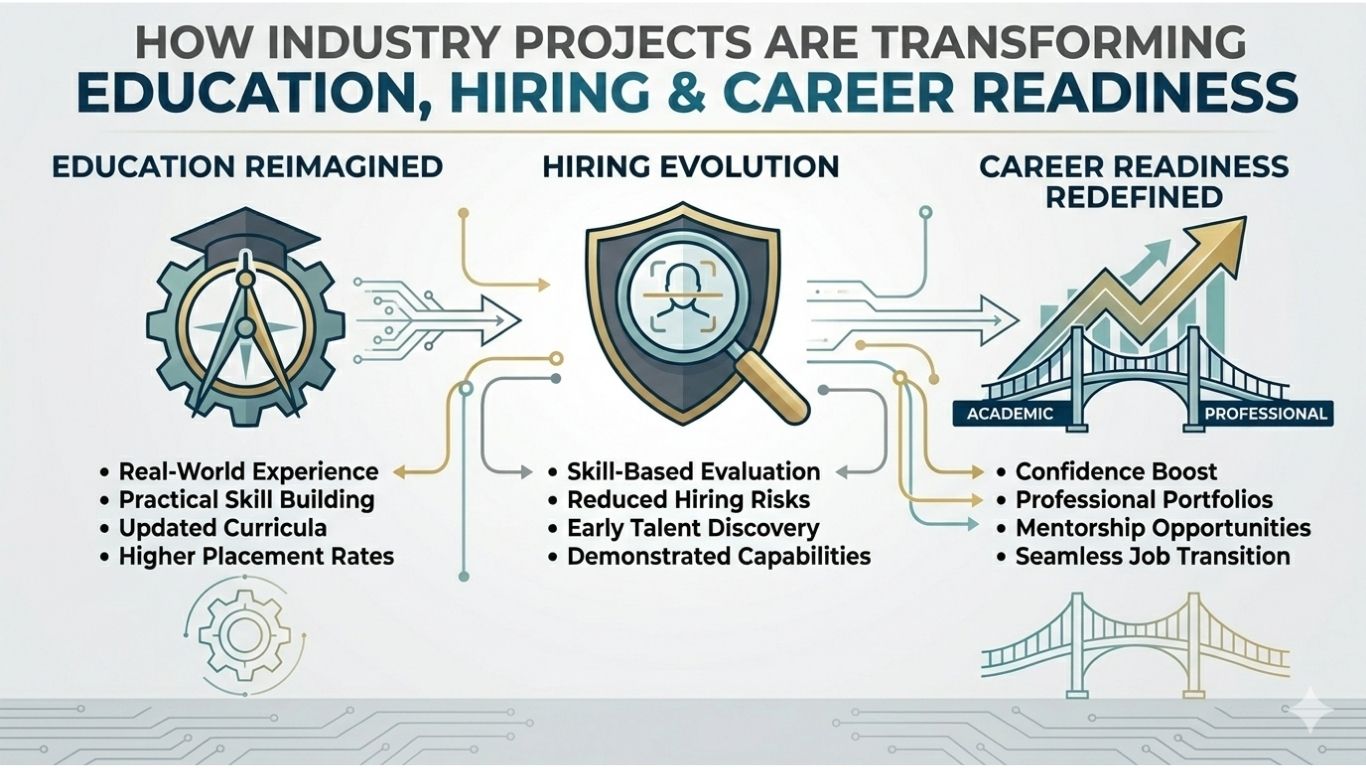
For decades, higher education has focused on academic learning – lectures, assignments, and examinations. But as industries evolve at record speed, employers no longer look for just degrees; they look for graduates with hands-on abilities, domain expertise, and real-world experience.
Universities are under growing pressure to prepare students who can apply what they’ve learned, adapt to professional environments, and deliver results from day one. The key lies in integrating live, employer-driven projects into academic frameworks – helping students move from theory to practice, and from classrooms to boardrooms seamlessly.
Why Industry Exposure Matters More Than Ever
A resume filled with grades no longer impresses employers. The ability to think, collaborate, and execute in real settings does.
Industry exposure ensures that students:
- Experience real business problems rather than case studies.
- Collaborate across disciplines and deadlines.
- Build the professional resilience that traditional teaching often overlooks.
This exposure transforms academic understanding into practical competence, equipping students with a tangible sense of accountability and ownership.
The Role of Live Projects in Skill Development
Live projects bridge academia and industry through assignments designed by real employers. They expose students to authentic workplace tools, workflows, and mentorship structures.
Through these projects, students develop:
- Hands-on problem-solving skills.
- Collaboration and communication abilities.
- Confidence in execution under real-world conditions.
Unlike internships that may lack structure, live projects ensure measurable outcomes, defined goals, and documented evaluations that align with academic credit systems.
Implementing Live Projects Effectively
1. Create a Structured Collaboration Framework:
Build formal partnerships with companies across industries. These should include project scoping, timelines, mentorship, and evaluation mechanisms.
2. Integrate Projects into Curriculum:
Treat live projects as academic components, ensuring credits or grades reflect the real work done.
3. Leverage Digital Platforms:
Platforms like Qollabb manage project allocation, mentor matching, and real-time evaluation dashboards, reducing operational load on faculty.
4. Adopt Rubric-Based Evaluation:
Use standardized rubrics to assess creativity, collaboration, and delivery quality.
5. Engage Alumni and Employers as Mentors:
Alumni mentorship enriches the experience by combining academic and professional insights.
The Institutional Impact
Universities that embed live projects in their academic model achieve:
- Enhanced reputation through demonstrable graduate outcomes.
- Compliance with UGC’s experiential learning guidelines.
- Sustained industry partnerships that go beyond placements.
- Improved employability through measurable project performance.
The Qollabb Model
Qollabb provides an end-to-end digital ecosystem where universities can onboard employers, manage live projects, assign mentors, and track progress. Each project generates analytics on student performance, enabling transparency, scalability, and compliance-ready documentation.
Students graduate not only with degrees but with verified industry experience that demonstrates their competence beyond the classroom.
Conclusion
By integrating real-world projects, universities can shift from producing degree-holders to developing industry-ready professionals. Live projects empower students to apply, adapt, and excel – turning theory into measurable outcomes and education into experience.